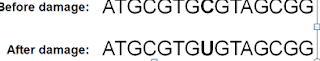Due to the presence of UV light, it might cause break in the sugar-phosphate backbone.
There are two types of break:
- Can be limited to one of the two strands (a single-stranded break, SSB) or
- on both strands (a double-stranded break (DSB).
Two types of breaks in the sugar phosphate backbone can also be caused by ionizing radiation. A single strand break occurs when only one of the sugar phosphate backbones is broken. Single strand breaks are readily repaired using the opposite strand as a template.
Double-strand are difficult to repair, they can cause mutations and cell death. Unrejoined double strand breaks are cytotoxic (they kill cells). Double strand breaks can also result in the loss of DNA fragments which, during the repair process, can cause the joining of non-homologous chromosomes (chromosomes not of the same pair).
When cells are exposed to sunlight, radiant energy can damage the DNA. One of the damage caused by the UV radiation is ultraviolet irradiation causes covalent bond formation between adjacent thymines on the same strand of DNA.
When DNA is damaged in this way, it cannot be replicated or transcribed because when the thymine and thymine form covalent bond, it will form a thymine dimers and creates a hump.